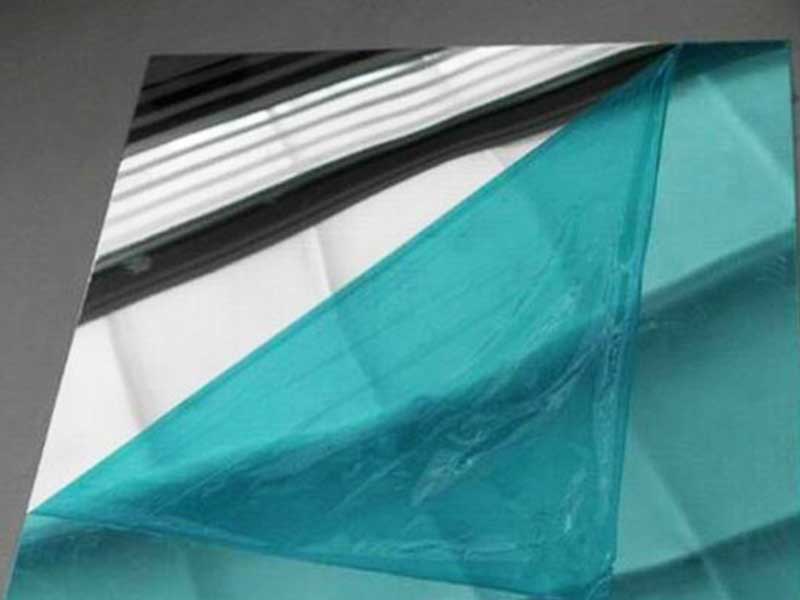
Anodized aluminum
Anodized aluminum
The oxidation treatment of aluminum and its alloys is divided into two major categories: chemical oxidation and electrochemical oxidation (commonly known as anodization). For the purpose of decoration, coloring treatment is often required, and the coloring method has chemical coloring and electrolytic coloring.
The film obtained by chemical oxidation treatment is relatively thin, generally has a thickness of 0.5 μm to 4 μm, and is soft and non-abrasion resistant, and has a lower corrosion resistance than an anodized film, and is generally not suitable for use alone. Because of the good adsorption capacity of the chemical oxide film, it mainly acts on the bottom layer of the paint.
The anodized oxide film is about 5-20 microns thick (hard anodized film thickness can reach 60-200 microns), has high hardness, good heat resistance and insulation, and has higher corrosion resistance than chemical oxide film. , porous, has a good adsorption capacity.
The chemical oxidation treatment requires simple equipment, convenient operation, high production efficiency and low cost, wide application range, and is not limited by the size and shape of the parts. It can oxidize large parts and assemblies (such as spot weldments, rivets, slender pipes). Wait). After chemical oxidation, it can effectively improve the corrosion resistance of the parts.
The overall performance of aluminum anodized film is superior to that of chemical oxide film, and its application is more extensive. The main uses are:
(1) Protective. Improve the wear resistance, corrosion resistance and weather resistance of parts.
(2) Decorative. The cost of the bright film is seen as a color film.
(3) Insulation. As a capacitor dielectric film, the aluminum coil insulation film can withstand a voltage of 25V per micron.
(4) Improve the adhesion to the organic coating for the bottom layer of the coating.
(5) Improve the bonding force with the inorganic coating layer, and make the bottom layer of electroplating and enamel.
(6) Other functional uses in development, depositing magnetic alloys as memory elements, solar absorption plates, ultra-high hard films, dry lubricating films, catalytic films, etc. in porous films.
Therefore, the oxidation treatment of aluminum and its alloys has been widely used in the construction, aerospace and aerospace industries, electrical and electronics industries, food industry, chemical and pharmaceutical industries, transportation and other fields. At the same time, with the development of these industries, their requirements for anodizing are getting higher and higher.